Understanding what is a fupa is important for anyone struggling with stubborn lower body fat. A FUPA, often called the fatty upper pubic area, refers to extra fat stored above the pubic bone and below the lower stomach. This area can look more visible due to genetic fat distribution, post-pregnancy body changes, or weight fluctuation effects over time.
Many people confuse it with belly fat, but it behaves differently and responds slowly to diet or exercise. The condition can affect both men and women, especially after childbirth, surgery, or major weight loss. Beyond appearance, it may cause discomfort, clothing issues, and emotional stress, making awareness and proper care essential.
What Is a FUPA? A Clear Medical Explanation
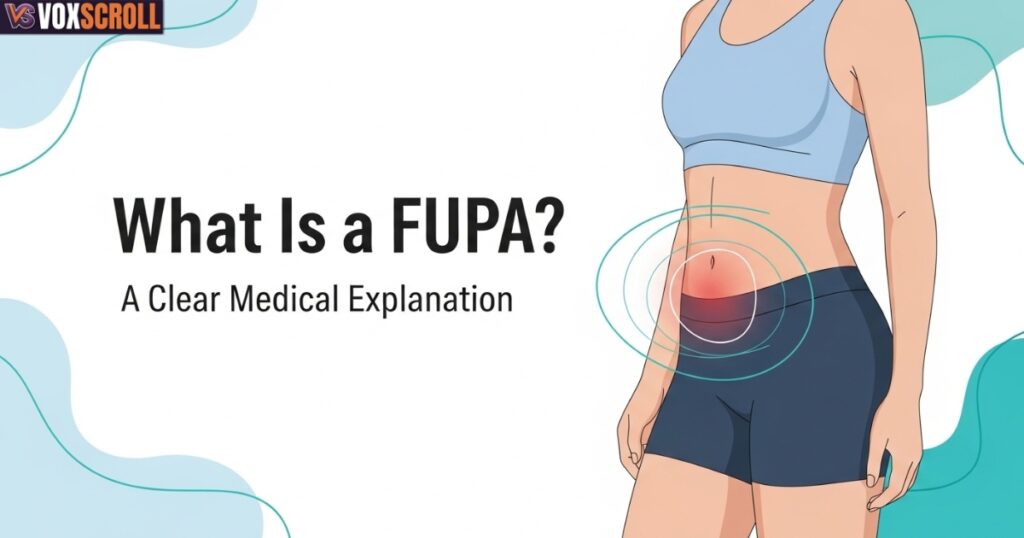
A FUPA, short for fatty upper pubic area, refers to soft tissue that sits above the pubic bone. Doctors describe it as fat accumulation above pubic area within the lower abdomen. This region exists for protection and stability, not aesthetics, which explains why it resists change.
The confusion around what is fupa comes from mixing anatomy with appearance. The lower abdomen contains subcutaneous fat accumulation, connective tissue, and skin. When these layers thicken or loosen, the area becomes more visible, especially in tight clothing or swimwear.
What Does FUPA Stand For?
FUPA stands for fatty upper pubic area, a term that entered popular culture before medicine adopted it. While informal, doctors now use it to explain concerns involving upper pelvic fat without judgment or stigma.
Clinically, this area cushions bones and organs. That fat protecting pubic symphysis plays a role in movement and impact absorption. The problem isn’t the fat itself but changes in volume, skin tension, or structure.
Where Is FUPA Located on the Body?
The FUPA sits in the infraumbilical zone between the belly button and pubic hairline. Anatomically, it overlaps the mons pubis and lower abdomen. Many confuse it with lower belly fat, but location matters.
This region includes mons pubis fat, skin, fascia, and ligaments. Changes here affect contour more than health, which explains why frustration is common despite normal lab results.
Read Also: Crackstube: Safety, Trends & Alternatives
Is FUPA Normal or a Medical Concern?
For most people, a FUPA is completely normal. Bodies store fat differently based on hormones, genetics, and age. Seeing FUPA in women after pregnancy or weight change is especially common.
Medical concern only arises when symptoms appear. Otherwise, this is a cosmetic and emotional issue, not a disease. Understanding that difference reduces fear and unrealistic expectations.
When FUPA Is Harmless
A harmless FUPA causes no pain, infection, or movement limits. It often reflects genetic fat distribution or natural aging. Many healthy people have visible FUPA tissue even at low body weight.
In these cases, reassurance matters more than treatment. Accepting normal variation aligns with a body neutrality perspective, which improves mental health outcomes.
When You Should Seek Medical Advice
Medical input matters when you experience infections in skin folds, discomfort, or hygiene issues. Difficulty walking, irritation, or difficulty cleaning genital area may signal excess tissue.
Doctors also evaluate sudden changes. Rapid growth could relate to metabolic signaling, hormones, or weight fluctuation effects, which deserve proper assessment.
What Causes FUPA? Key Factors Explained
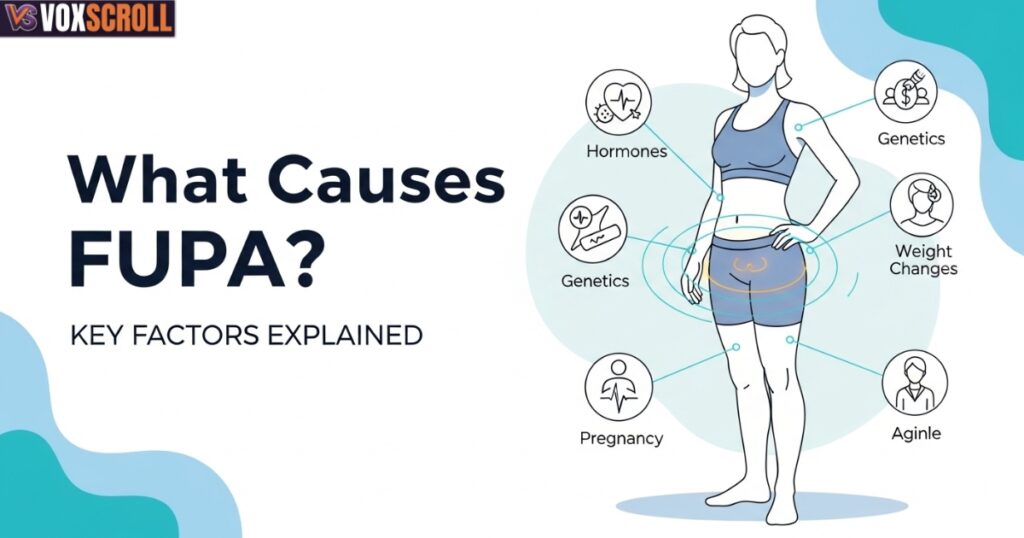
Understanding FUPA causes helps you avoid ineffective solutions. This area responds slowly to dieting because hormones and fascia influence it more than calories alone.
Most causes overlap. Rarely does one factor act alone. Instead, lifestyle, biology, and structure interact over time.
Genetics and Body Fat Distribution
Genes strongly affect pelvic fat distribution. Some families store fat lower, others centrally. Studies show identical twins share similar FUPA patterns regardless of diet.
This explains why stubborn lower abdominal fat persists even with exercise. Biology sets the baseline before behavior plays a role.
Hormonal Imbalances and Weight Changes
Hormones dictate storage. Estrogen cortisol fat storage shifts fat toward the pelvis under stress or estrogen dominance. Insulin sensitivity also affects how fat cells respond.
Chronic stress triggers cortisol stress response, slowing fat release in this region. That’s why aggressive dieting often worsens appearance rather than improving it.
Pregnancy, C-Sections, and Aging
Pregnancy stretches fascia and skin permanently in many cases. Post-pregnancy body changes often include laxity rather than fat alone.
After surgery, especially FUPA after C-section, scar tension alters tissue position. Aging further reduces elasticity, leading to loose skin above public area.
Read Also: Your Topics Multiple Stories: Powerful Insights & Strategies
Common Symptoms and How FUPA Develops Over Time
Typical fupa symptoms include visible bulging, skin creases, and discomfort in tight clothing. Over time, gravity and lax fascia exaggerate the contour.
Emotionally, many report embarrassment due to pubic fat. This psychological strain often outweighs physical issues and drives searches for how to fix a fupa.
FUPA vs Lower Belly Fat: What’s the Difference?
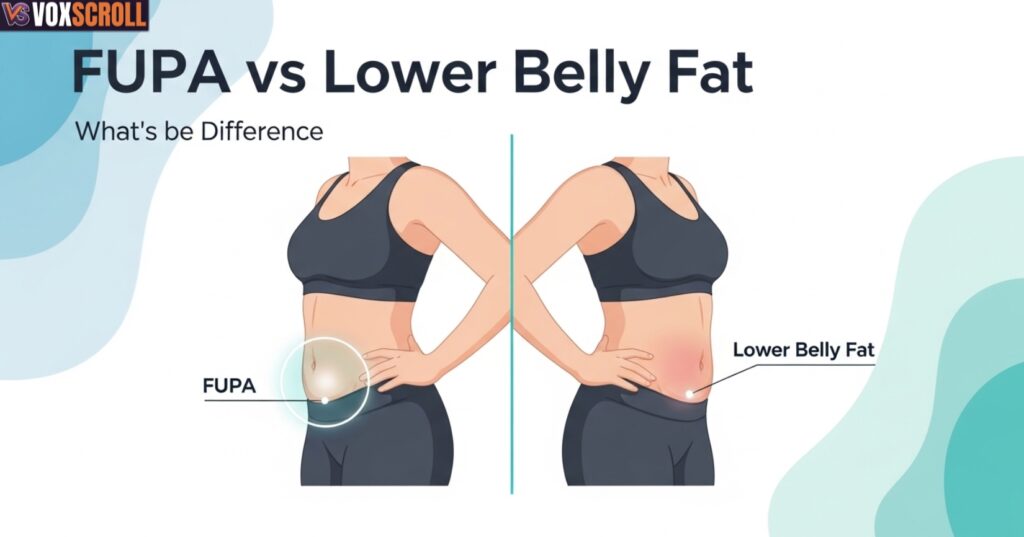
The key distinction in fupa vs belly fat lies in depth. Belly fat often includes visceral fat vs subcutaneous fat, which responds faster to weight loss.
FUPA tissue is mostly superficial and structural. That’s why waist size drops before the pubic area changes, frustrating many people.
Can You Reduce FUPA Naturally?
Natural fupa reduction methods focus on whole-body change, not spot reduction. While fat cells can shrink, fascia and skin adapt slowly.
Success depends on patience, consistency, and realistic goals. Natural improvement is possible but gradual.
Diet and Nutrition for FUPA Reduction
Nutrition supports body recomposition rather than targeted fat loss. High protein preserves muscle while stabilizing insulin. Avoid inflammatory foods and bloating, which exaggerate appearance.
Timing matters. Balanced meals support hormone-aware fat loss better than extreme restriction.
Exercises That Target the Lower Abdomen
No exercise burns FUPA fat directly. However, core stability improves posture and reduces protrusion. Fascia training and controlled resistance support tissue integrity.
Improved posture and pelvic alignment often creates visible improvement before fat loss occurs.
Lifestyle Changes That Actually Help
Sleep, stress control, and weight stability matter more than endless workouts. Avoid weight gain after surgery or crash diets that damage skin.
Consistency beats intensity when addressing structural fat storage.
Read Also: Ashenaletuve 2026: Powerful Insights, Uses & Future Impact
Non-Surgical FUPA Treatment Options
Modern FUPA treatment options include technology-based contouring. These methods reshape rather than cure.
They work best for mild to moderate cases without severe skin laxity.
Fat-Freezing and Body Contouring
Cryolipolysis and radiofrequency target fat cells using cold or heat. Results show 15–25% reduction per session in selected patients.
These methods fall under non-invasive body contouring and require multiple sessions for visible change.
Skin Tightening Procedures
Energy-based devices improve mild laxity. Laser fat reduction also stimulates collagen, improving firmness.
These options suit people with good muscle tone and minimal excess skin.
Surgical Treatments for FUPA
When structure dominates, FUPA plastic surgery offers predictable results. Surgery addresses fat, skin, and attachment points.
Choosing a board-certified plastic surgeon ensures proper evaluation and safety.
Liposuction for FUPA
FUPA liposuction removes pubic mound fat when skin elasticity is good. Surgeons often perform pubic area liposuction through hidden incisions.
Results depend on stable weight and healthy tissue quality.
Mini Tummy Tuck vs Full Tummy Tuck
A mini tuck targets lower laxity, while a full abdominoplasty procedure addresses muscle separation. Tummy tuck FUPA correction often combines both.
Some cases require monsplasty surgery or pubic lift surgery for optimal contour.
Post-Surgery Recovery and Healing Timeline
Fupa surgery recovery varies by procedure. Swelling and bruising peak early, then fade gradually. Compression garments after surgery support healing.
Most patients resume light activity within weeks. Final FUPA surgery results appear after several months.
Risks, Results, and Long-Term Prognosis
Risks include infection, scarring, or uneven contour. Proper technique minimizes complications. Long-term surgical outcomes remain stable if weight stays consistent.
Surgery offers the closest option to a permanent solution for FUPA, but lifestyle still matters.
Should You Travel Abroad for FUPA Treatment?
Medical tourism appeals to cost-conscious patients. However, aftercare challenges exist, especially for traveling patients for surgery.
Continuity of care often outweighs savings, especially for complex procedures.
Medical Tourism Pros and Cons
Lower upfront cost competes with limited follow-up. Communication barriers increase risk during complications.
Choosing a board certified plastic surgeon locally often improves safety and satisfaction.
Cost Comparison and Safety Tips
U.S. procedures cost more but include structured follow-up. Always verify credentials, facility accreditation, and emergency protocols.
Never choose surgery based on price alone.
FAQs – What is a Fupa
What is a FUPA in simple terms?
A FUPA is extra fat stored above the pubic area and below the lower stomach.
What does a FUPA look like?
A FUPA appears as a soft or rounded bulge of fat just above the pubic area, below the lower abdomen.
What is a FUPA caused by?
It is caused by genetics, hormone-related fat storage, pregnancy, C-sections, and weight changes.
What causes a woman to have a FUPA?
Common causes include genetics, hormone-related fat storage, pregnancy, C-sections, aging, and weight fluctuation effects.
Does FUPA ever go away?
A FUPA can reduce with fat loss, body recomposition, or targeted treatment, but it may not disappear fully for everyone.
What is a FUPA after pregnancy?
After pregnancy, FUPA often appears from post-pregnancy body changes, loose skin, and fat redistribution above the pubic area.
Is FUPA just belly fat?
No, FUPA is upper pelvic fat in the infraumbilical region, which behaves differently than general lower belly fat.
Will losing weight remove FUPA?
Weight loss can help, but stubborn lower abdominal fat may remain due to genetic fat distribution and hormones.
What is the unhealthiest body shape?
Health risk depends more on visceral fat vs subcutaneous fat, not body shape alone, with abdominal fat being most concerning.
What is a FUPA on a woman’s body?
In women, a FUPA appears as fullness in the upper pelvic area, often more visible after childbirth.
What is a FUPA and can it be removed naturally?
A FUPA can sometimes be reduced naturally, but stubborn cases may need targeted treatment.
What is a FUPA after pregnancy?
After pregnancy, FUPA often appears from post-pregnancy body changes, loose skin, and fat redistribution above the pubic area.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right FUPA Solution
FUPA explained clearly shows this is not a failure. It reflects hormones, structure, and time. The best fupa treatment depends on your body, not trends.Whether you choose acceptance, lifestyle change, or surgery, a personalized treatment plan guided by science delivers the best outcome.
Welcome to VoxScroll! I’m Ali Hussnain, an AI-Powered SEO, and Content Writer with 2 years of experience.
I help websites rank higher, grow traffic, and look amazing. My goal is to make SEO and Web design Simple and effective for everyone.
Let’s Achive more together!

